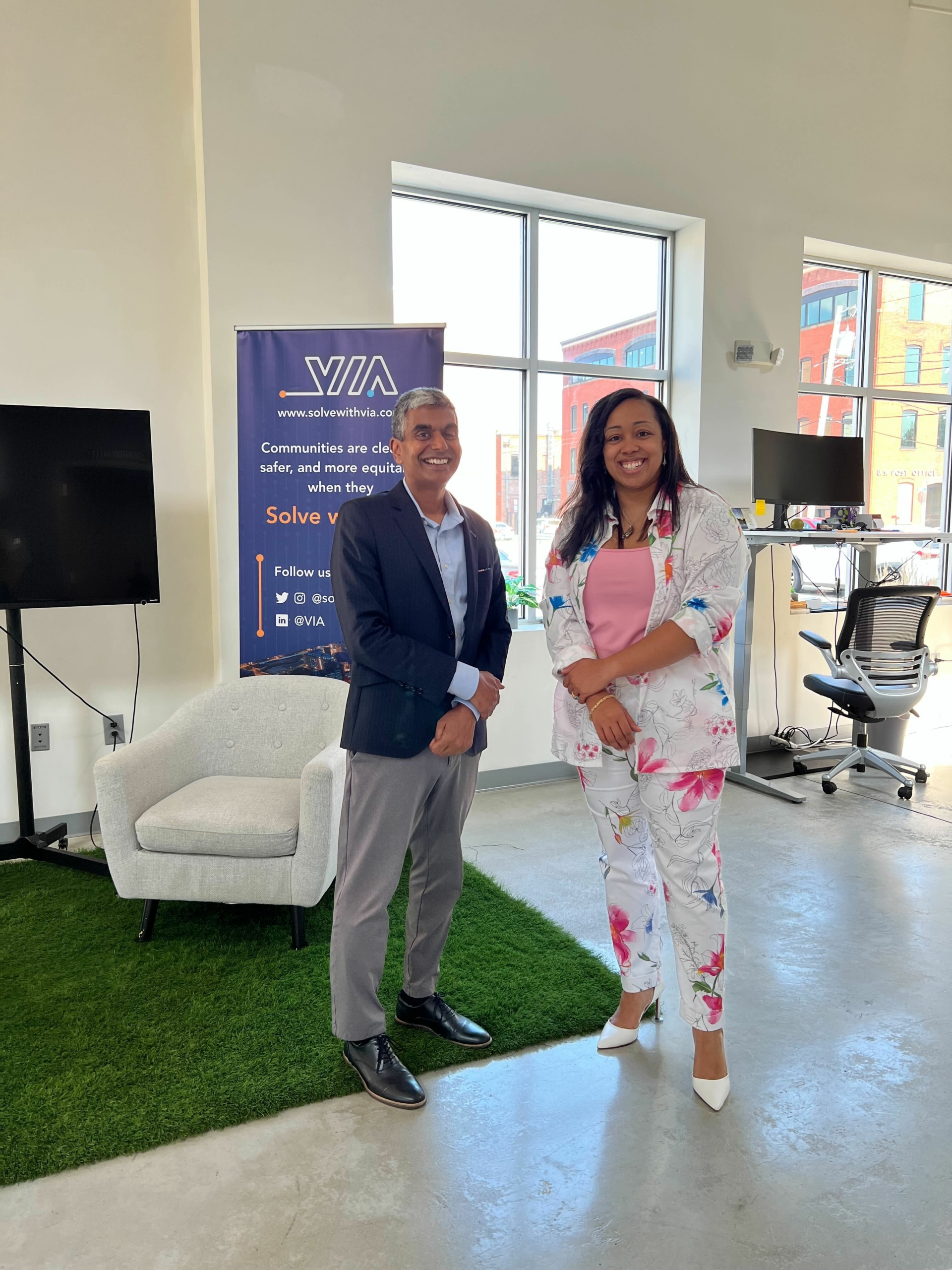
Last month, VIA’s CEO, Colin Gounden and Client Delivery Lead, Becky McClements ventured across the Atlantic to meet our Lead Software Research Architect, Madjid Aoudia in none other than, Switzerland 🇨🇭!
The trio had an action-packed week that is well worth the recap for our devoted VIA followers. So, who is ready to take an adventure with us from Zug to Davos?
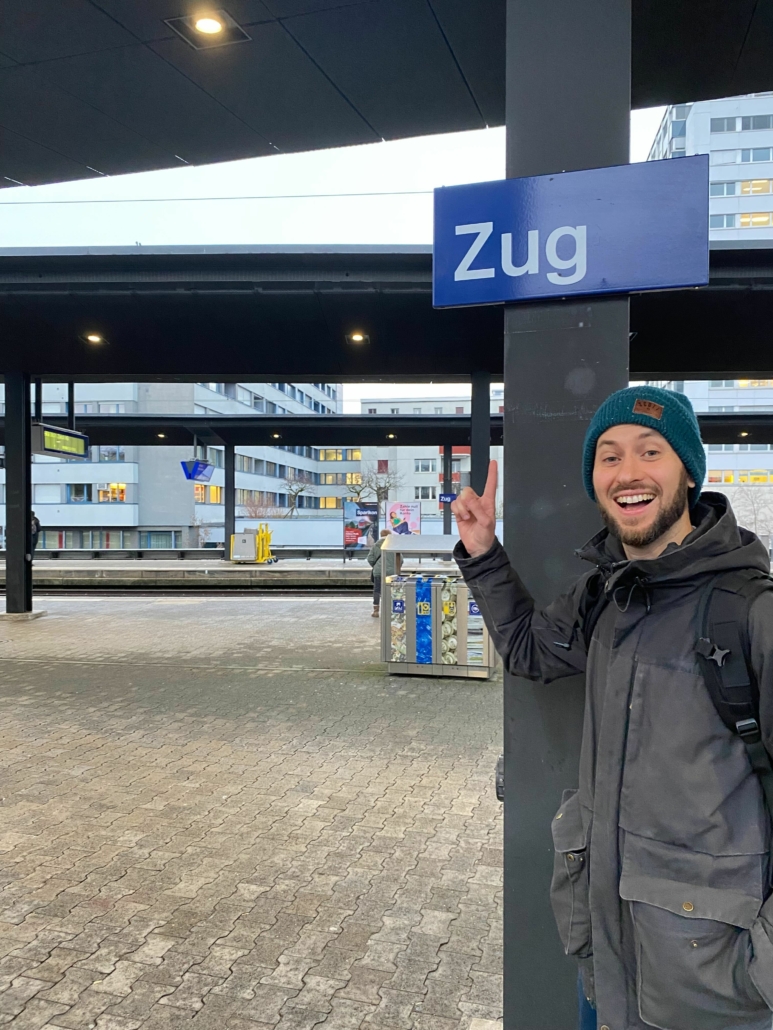
Day 1: Zug
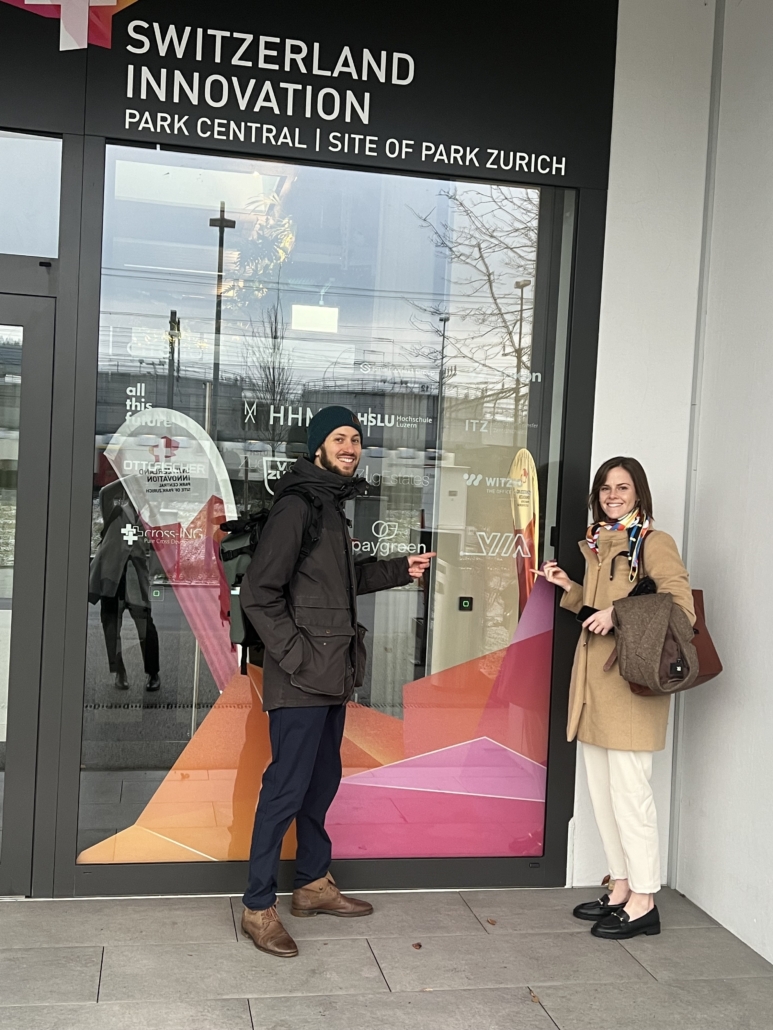
If you are new to VIA’s blog or just need a refresher, there are many reasons why we chose Switzerland as our European headquarters: clean energy, data privacy, and blockchain, our wheelhouse! Once our team landed in Switzerland, it was off to our office in Zug by train. Madjid and Becky also took the opportunity to snap a picture of our logo on the outside of the office, too!

Madjid Aoudia ready for his trip to Zug.

Madjid and Becky McClements at VIA’s European headquarters.
Then, we met with one of our energy customers for a full-day workshop at our office, followed by dinner with executives in the utility space.
Day 2: Zurich + Lucerne
We kicked off day two in: Zurich! Our team met with government entities to discuss how we can support their data privacy initiatives. With a new data privacy code of conduct coming into effect in January, two agencies reached out to VIA for our expertise in data privacy. We look forward to continuing the conversation and deepening our support for Swiss data privacy efforts.
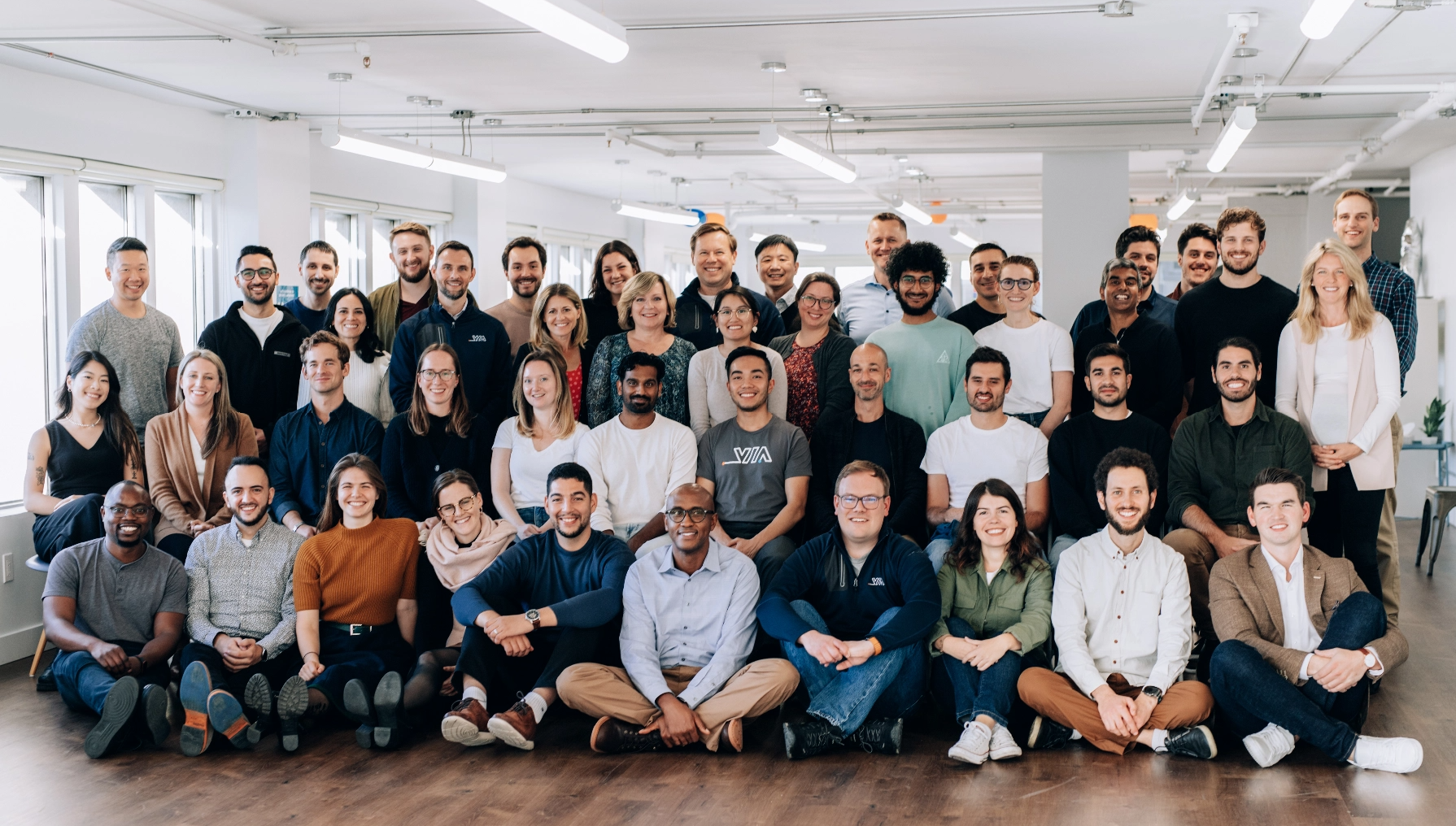
Later that day, we made our way to Lucerne, home of the HSLU iHomeLab. As we mentioned in our blog from 2022, “The year in Switzerland,” HSLU has been one of our research partners in energy and data privacy since 2018. We were thrilled to see the research they have been doing in energy efficiency and IoT and to have our Expansion Manager, Ray Neubauer join us!

VIA’s team alongside the iHomeLab team.

Colin at iHomeLab.
Finally, to cap the night off, we had dinner with executives in the electric vehicle and automotive space. Stay tuned for more on this front!
Day 3: Davos
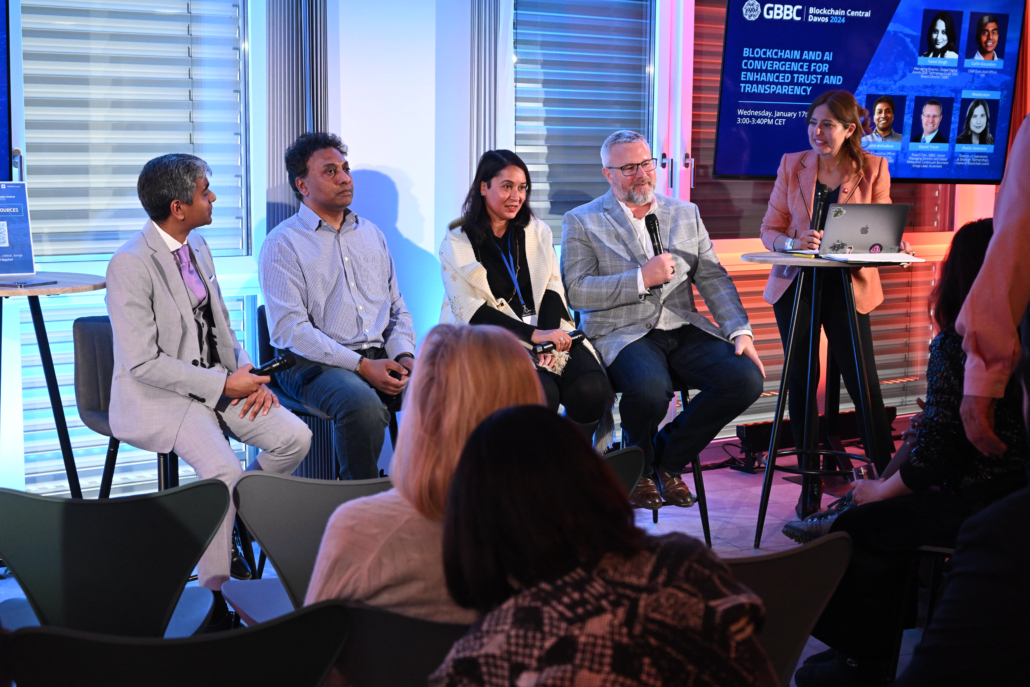
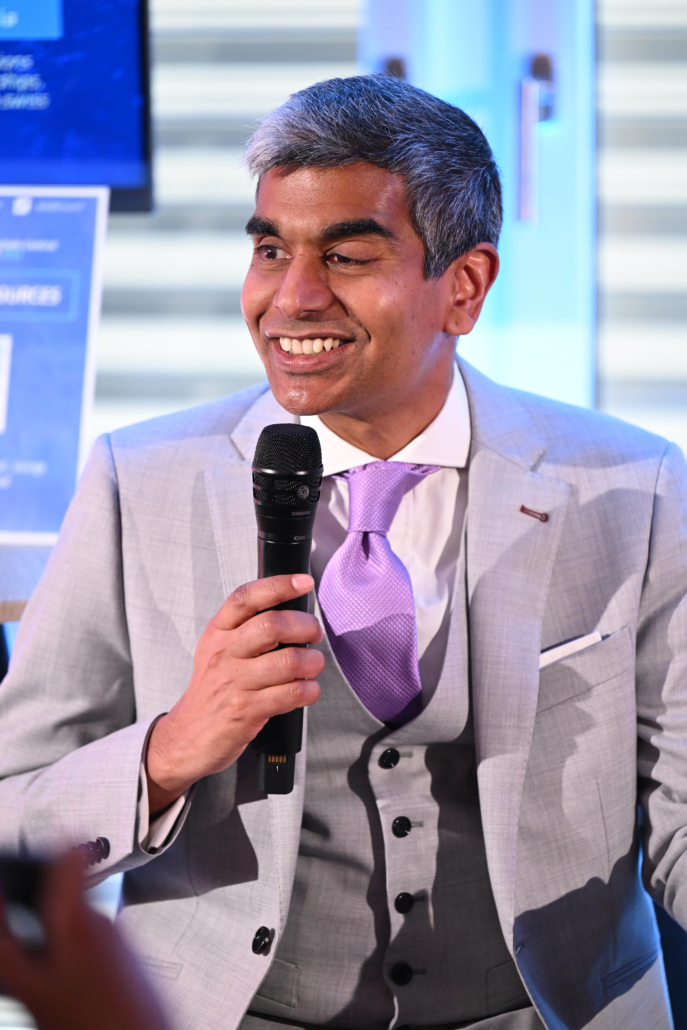
The highlight of our week was traveling to Davos for the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC)’s 7th Annual Blockchain Central Davos event, hosted in parallel to the World Economic Forum. Colin was invited to speak on the panel, “Blockchain and AI Convergence for Enhanced Trust and Transparency” alongside Tanvi Singh, Managing Director, Global Digital Assets Technology Lead, UBS, John deVadoss, Co-Founder & CEO, NeuralFabric.ai, and David Treat, Board Chair, GBBC; Senior Managing Director and Global Metaverse Continuum Business Group Lead, Accenture.
Paola Valencia, Director of Operations, & Strategic Partnerships, Home of Blockchain.swiss, was the moderator, who did a fantastic job of keeping the conversation flowing and asking terrific questions. If you are short on time, don’t miss our favorite moments at the timestamps from the recording below:
- 9:23: Watch Colin introduce himself and VIA in Swiss German!
- 19:08: Paola says she was thrilled to see Colin’s name on the panel because she wanted to hear how VIA has been using AI and blockchain with actual companies and how those use cases impact humanity.
- 35:40: Colin provides his thoughts on the next big thing in the next six months related to AI and blockchain.
Thank you again to GBBC! The whole event from start to finish was world class and we are grateful for the opportunity (and the high quality pictures below 😉).
Day 4: Wrap up!
After the eventful day in Davos, not to mention the fact that we ran into people we know from Boston, San Francisco, and Washington, D.C. (the Americans were out in full force!), we closed out our trip by meeting with another automaker and more government officials in the evening.
As we reflect on the week, we wanted to acknowledge a few small things that make a big difference. Everywhere we went, there was next-level hospitality, people made time in any way they could to meet with us, and embraced VIA with open arms. All of these points keep us coming back (and the spectacular scenery isn’t too bad either!).
This trip laid the groundwork for what is sure to be some exciting announcements this year 📣.

View of the mountains during our train ride.